Sweet potatoes are a true culinary and nutritional powerhouse, beloved for their natural sweetness, versatility, and impressive health benefits. Often called “superfoods,” they’re packed with antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals, making them one of the most nutrient-dense plant-based foods you can enjoy. Beyond their flavor and nutrition, sweet potatoes have a fascinating history and play an important role in cuisines around the world.
From their ancient origins to their many uses in both sweet and savory dishes, sweet potatoes offer so much to discover. Here are some key facts that highlight their benefits, history, and versatility!
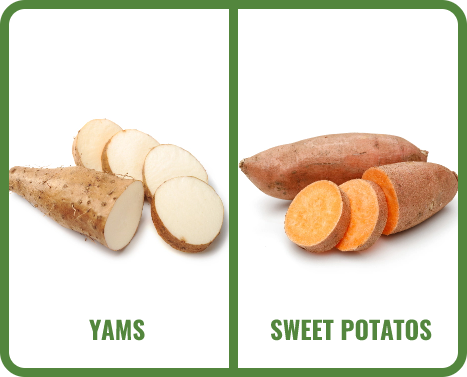
Sweet potatoes and yams are often confused, but they are not the same. While both are starchy tubers, they belong to different plant families. Sweet potatoes belong to the Convolvulaceae family, while yams belong to the Dioscoreaceae family.
In the U.S., the term “yam” is often used to describe orange-fleshed sweet potatoes, but true yams are typically starchy and have a rough, dark bark-like skin.
One medium sweet potato provides over 400% of your daily recommended intake of vitamin A, primarily in the form of beta-carotene, which supports eye health, immune function, and skin health.
Rich In Fibre They contain both soluble and insoluble fiber, promoting digestive health and helping to regulate blood sugar levels.
Sweet potatoes are a great source of vitamin C, manganese, potassium, and B vitamins, including B6 and folate.
Sweet potatoes are naturally low in fat and provide a good source of carbohydrates that can help keep you energized.
The most common variety in the U.S., these are sweet and creamy when cooked.
Less sweet than orange-fleshed varieties, they have a more neutral flavor and are often used in savory dishes.
These have a slightly nuttier flavor and are rich in anthocyanins, the same antioxidants found in blueberries.
These have a purple skin with white flesh and are sweeter and denser in texture than typical varieties.

The high levels of vitamin A (in the form of beta-carotene) are crucial for maintaining healthy vision, boosting the immune system, and promoting healthy skin.

Sweet potatoes are rich in antioxidants, such as beta-carotene and anthocyanins, which help reduce inflammation in the body.

Despite being starchy, sweet potatoes have a relatively low glycemic index (GI), meaning they release sugar slowly into the bloodstream and can help with blood sugar control.
Sweet potatoes are grown in many parts of the world, and they thrive in warm climates. Some of the largest producers are:
The largest producer of sweet potatoes in the world.
Particularly in the South (North Carolina, Louisiana, Mississippi, and California are major growing areas).
Sweet potatoes are a staple in many parts of Africa and are also popular in countries like Honduras and Nicaragua.
Sweet potatoes have been cultivated for thousands of years:
They are believed to have originated in Central or South America and were cultivated by indigenous peoples long before European contact.
Evidence of sweet potato cultivation dates back to over 5,000 years ago in the Americas.
The crop was later introduced to Europe and Asia in the 16th century by explorers, including Christopher Columbus
While sweet potatoes are often used in sweet dishes (like casseroles, pies, and baked goods), they are also incredibly versatile in savory dishes. They can be roasted, mashed, grilled, or even used in soups, stews, and salads.
Sweet potatoes have a relatively long shelf life compared to other root vegetables. When stored properly in a cool, dry place (like a pantry), they can last for several weeks, and sometimes even up to 1-2 months.
Sweet potatoes are a sustainable crop:
They are relatively drought-resistant, making them ideal for regions with lower water availability.
Sweet potatoes grow well in many different soil types, and their vines can also be used as fodder for livestock.
Sweet potato leaves are also edible and highly nutritious, often used in salads or stir-fries in some parts of the world.
Sweet potatoes are used in diverse ways across different cultures:
In Africa, sweet potatoes are often boiled, mashed, or fried and served alongside stews.
In Asia, sweet potatoes are used in both sweet and savory dishes, from desserts like Japanese sweet potato tarts to savory dishes like sweet potato tempura.
In the Caribbean, sweet potatoes are frequently included in savory stews, curries, and baked dishes.
In Latin America, sweet potatoes are common in both savory and sweet preparations, such as “camote” (sweet potato) dishes in Mexico, often paired with beans, corn, or chicken.





246 CR 446
Vardaman, MS
38878